

About
1. Who is a candidate for partial knee replacement?
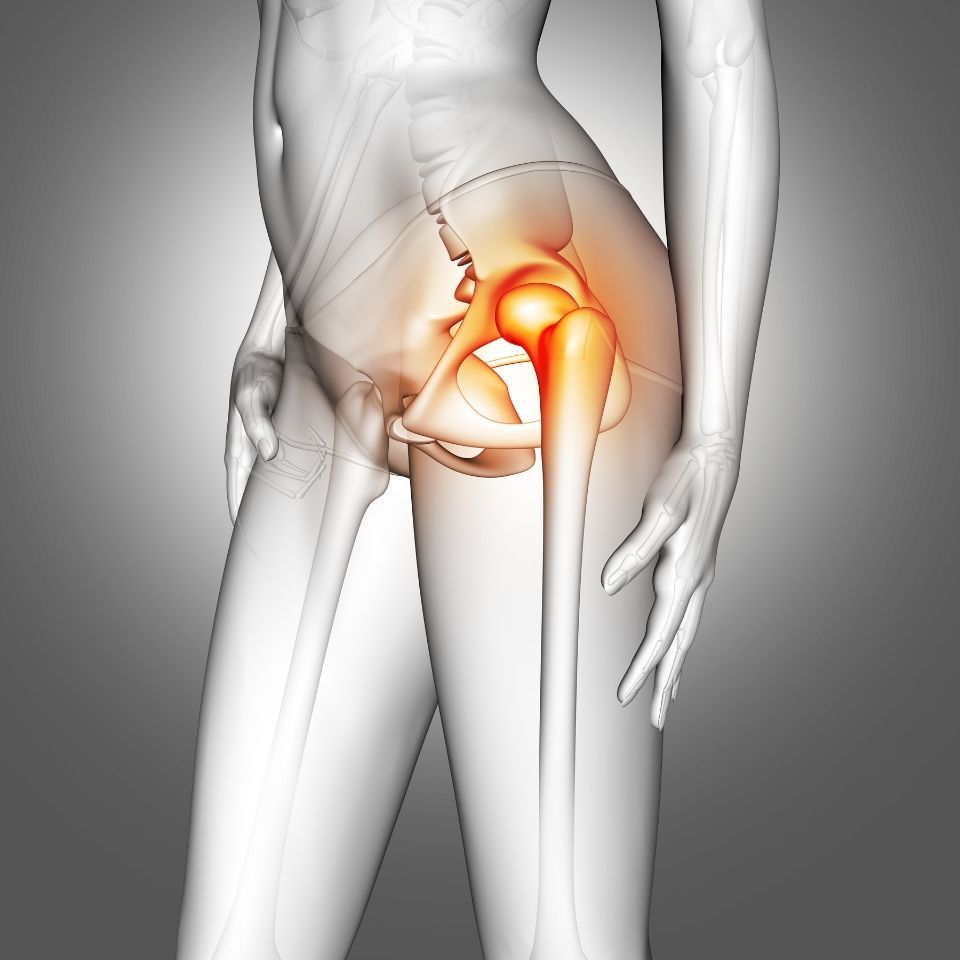
The knee joint consists of three compartments: the medial, lateral, and patellofemoral compartments (the area in contact with the kneecap). Partial knee replacement refers to the procedure of replacing just one or more of these compartments individually with prostheses.
This option is generally suitable for patients where cartilage loss is limited to a single compartment and the other areas are relatively healthy, with intact ligaments.
Typically, these patients are more active, have higher expectations from their knee function, and engage in recreational sports, using their knees in diverse angles and directions.
In contrast, total knee replacement is often recommended for more sedentary individuals, whose main goals are painless walking and climbing stairs, rather than engaging in sporting activities.
The most commonly damaged compartment in the knee is the medial (inner) compartment, as it bears approximately three-quarters of the load across the knee joint.
Factors such as congenital deformities, obesity, physical inactivity, and meniscus tears can cause load concentration especially in the inner compartment, leading over time to irreversible cartilage damage.
2. How is it determined whether a patient is suitable for partial knee replacement?
Patients with widespread pain throughout the knee, those with inflammatory arthritis, or those with ligament instability are generally not suitable candidates for partial knee replacement.
3. What is the surgical process for partial knee replacement?
Preoperative preparations are similar to those for total joint replacement surgeries. Preoperative tests are typically performed one or several weeks before hospital admission. After evaluating general health and adjusting medications, surgery is scheduled with anesthesiology approval.
The surgery usually requires a one or two-night hospital stay. Through a 10-centimeter incision based on the affected compartment, worn-out tissues are removed, the bone is prepared, and metal components are implanted. A polyethylene insert is placed to provide a smooth gliding surface.
The procedure is most commonly performed under spinal or epidural anesthesia with sedation, but general anesthesia can also be used if necessary. Pain control post-surgery is managed with epidural catheters, nerve blocks, pain pumps, and intraoperative local anesthetic injections.
4. Is postoperative pain severe after partial knee replacement?
Pain control strategies include epidural catheters, nerve blocks under ultrasound guidance, intraoperative joint injections, preemptive analgesia, and regular postoperative pain medications.
The majority of patients do not experience significant problems with pain control after surgery, and the need for additional interventions or hospital readmission due to pain is below 2%.
5. Is blood transfusion necessary after knee replacement surgery?
Blood transfusions are required in only 1–2% of cases following surgery. Thanks to techniques like the use of tranexamic acid, controlled hypotension, and improved surgical methods, transfusion rates have dramatically decreased from around 90% in the past to approximately 12% today.
Patients with significant preoperative anemia are more likely to need transfusion.

Treatments
Total Knee Replacement
Total Knee Replacement
Total Hip Replacement
Total Hip Replacement
Hip Revision Arthroplasty
Hip Revision Arthroplasty
Knee Revision Arthroplasty
Knee Revision Arthroplasty
Hip Osteotomy
Hip Osteotomy
Hip Dislocation
Hip Dislocation
Avascular Necrosis (AVN)
Avascular Necrosis (AVN)
Hip Arthritis
Hip Arthritis
Knee Arthritis (Gonarthrosis)
Knee Arthritis (Gonarthrosis)
Hip Fracture
Hip Fracture
Total Ankle Replacement
Total Ankle Replacement
Total Shoulder Replacement
Total Shoulder Replacement